Science, Technology, and Society LET REVIEWER
General Education
Lesson 15: Excretory System
(Human Systems)
The excretory system removes waste products
made by the body. These wastes come from normal activities like digestion and
energy use. Without this system, wastes would build up and harm the body. It
helps keep the body clean and balanced, just like how taking out trash keeps a
house tidy.
Main Functions or Main Ideas
- The main
function of the excretory system is to remove metabolic
waste from the body.
- It
helps maintain water balance and salt balance in
the body.
- This
system also removes extra water and toxins made during
metabolism.
- Wastes
are released from the body as urine, sweat,
or carbon dioxide (from the lungs).
Keeping a balance of water and salts is called homeostasis,
which is vital for all body functions.
Major Parts
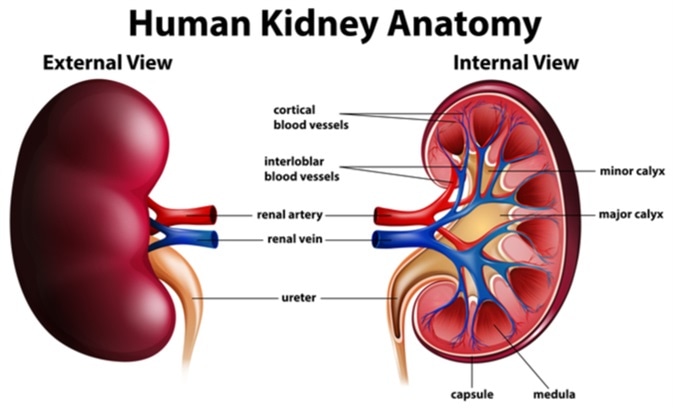
1. Kidneys
- The kidneys are
two bean-shaped organs located on both sides of the spine in the lower
back.
- Their
main job is to filter blood, removing waste and extra water to
form urine.
- Each kidney has about one million small filtering units called nephrons.
- The kidneys act like a water filter, cleaning your blood by removing unwanted substances.
2. Ureters
- Ureters are
thin tubes that carry urine from each kidney to the urinary
bladder.
- They constantly move urine using smooth muscle movements.
- Ureters are like pipes that carry urine from kidneys to the bladder.
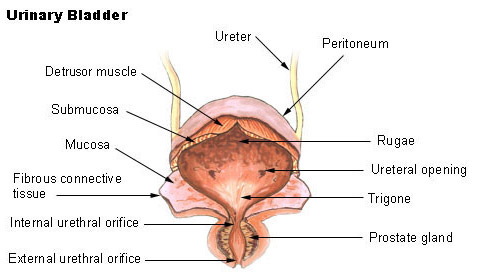
3. Urinary Bladder
- The urinary
bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine until it is released.
- It can stretch and hold about 400–600 mL of urine.
- The bladder works like a storage tank for urine.
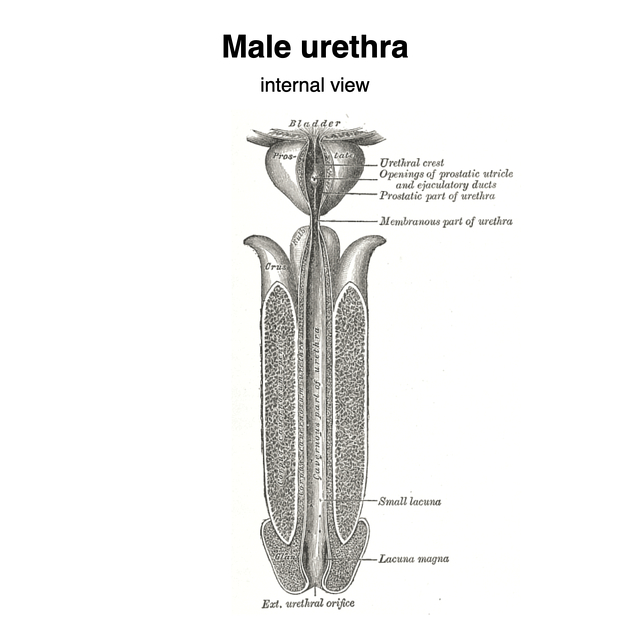
4. Urethra
- The urethra is
a small tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the
body.
- When you urinate, muscles around the bladder relax to let urine out.
- The urethra is the body’s exit path for urine.
Osmosis and Water Balance
a. Cell in Hypotonic Solution
- The
solution has less solute than inside the cell.
- Water
moves into the cell.
- The
cell swells and may burst (lysed).
Clue: Swell, Burst, Lysed
b. Cell in Isotonic Solution
- The
solution has the same solute concentration as inside the
cell.
- There
is no net movement of water in or out.
- The
cell stays normal in shape.
Clue: Balanced, Stable
c. Cell in Hypertonic Solution
- The
solution has more solute than inside the cell.
- Water
moves out of the cell.
- The
cell shrinks and becomes dehydrated.
Clue: Shrink, Shrivel, Dehydrated
Excretory System Quiz: click here