Science, Technology, and Society LET REVIEWER
General Education
Lesson 16: Integumentary System
(Human Systems)
What is the
integumentary system?
The integumentary
system is made up of the skin, hair, nails,
and glands found in the skin. These parts work together to cover and protect
everything inside the body. The skin is the largest organ of
the human body and forms the first line of defense against the outside world.
- The integumentary system is your body’s outside cover mainly your skin, plus hair and nails that protects everything inside.
 |
| Image from WisTech Open |
Main
functions
- Body covering - the skin wraps around the entire body and separates the
inside from the outside. It prevents dirt, germs, and many chemicals from
easily entering the body.
- Protects us from UV rays - the skin contains a pigment called melanin that
absorbs and blocks some of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays,
helping to protect deeper tissues.
- Physical protection - skin, hair, and nails cushion and
shield underlying muscles, bones, and organs from
bumps, cuts, and scrapes.
- Helps control body temperature - when you are hot, sweat glands in the skin make
sweat, and blood vessels near the surface widen so heat can escape. When
you are cold, blood vessels narrow to keep heat inside.
The integumentary
system covers the body, protects it from the sun and germs, and helps
keep your temperature just right.
Parts of the
integumentary system
 |
| Image from Healthline |
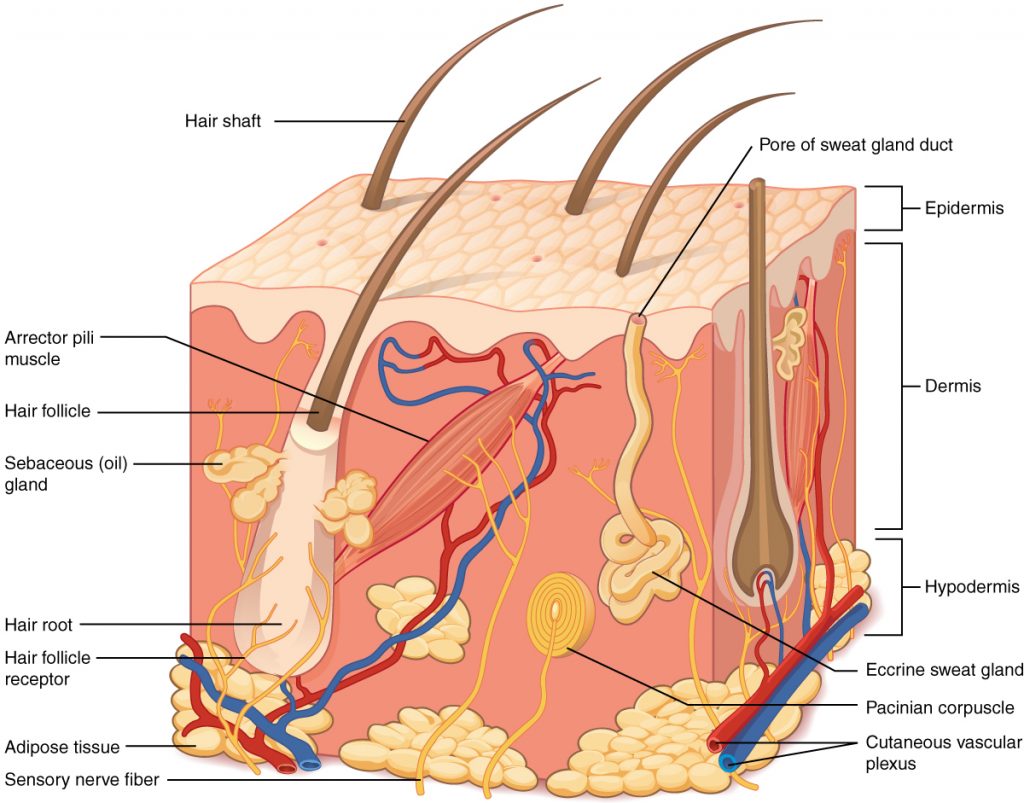
The skin is
the largest organ of the human body and has three main layers.
- Epidermis - thin, outer layer of skin made mostly of dead cells. It forms a tough protective shield and contains melanin, which gives skin its color and helps block UV rays.
- Dermis - thicker middle layer that contains blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, sweat glands, and oil glands. It provides strength, flexibility, and sensation (touch, pain, temperature).
- Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) - inner layer made mainly of fat and connective tissue. It helps insulate the body and protects deeper organs from blows.
The skin has layers: a thin outer shield, a thicker middle working layer, and a soft, fatty layer that cushions and warms you.
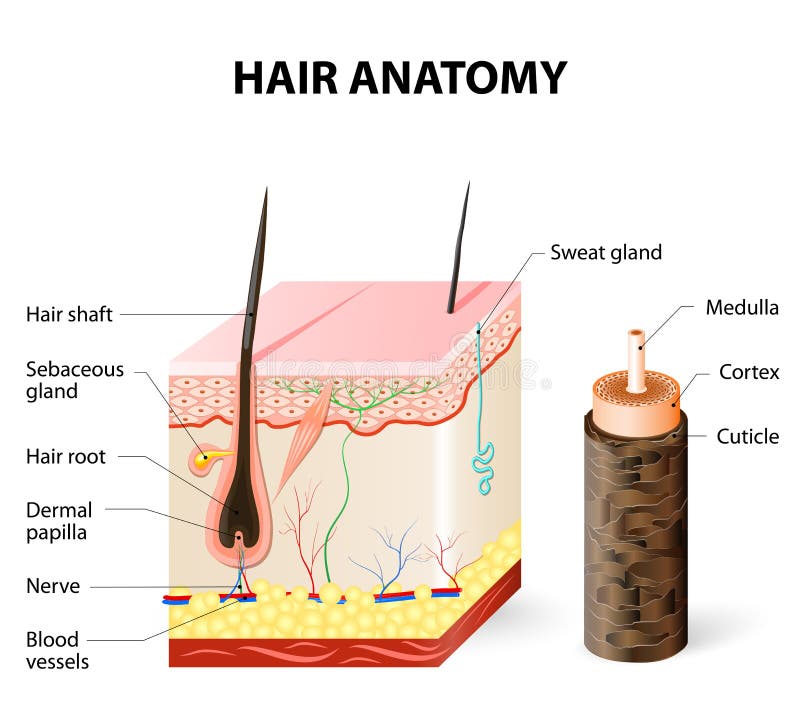
Hair is a thread-like structure that
grows from hair follicles in the skin.
 |
| Image from Dreamstime |
- Helps protect the scalp from UV
rays and from losing too much heat.
- Eyelashes and eyebrows keep
dust and sweat out of the eyes.
- Tiny hairs in the nose help
filter the air you breathe.
Hair on
your body helps protect you. For example, hair on your head blocks some sun and
helps keep you warm.
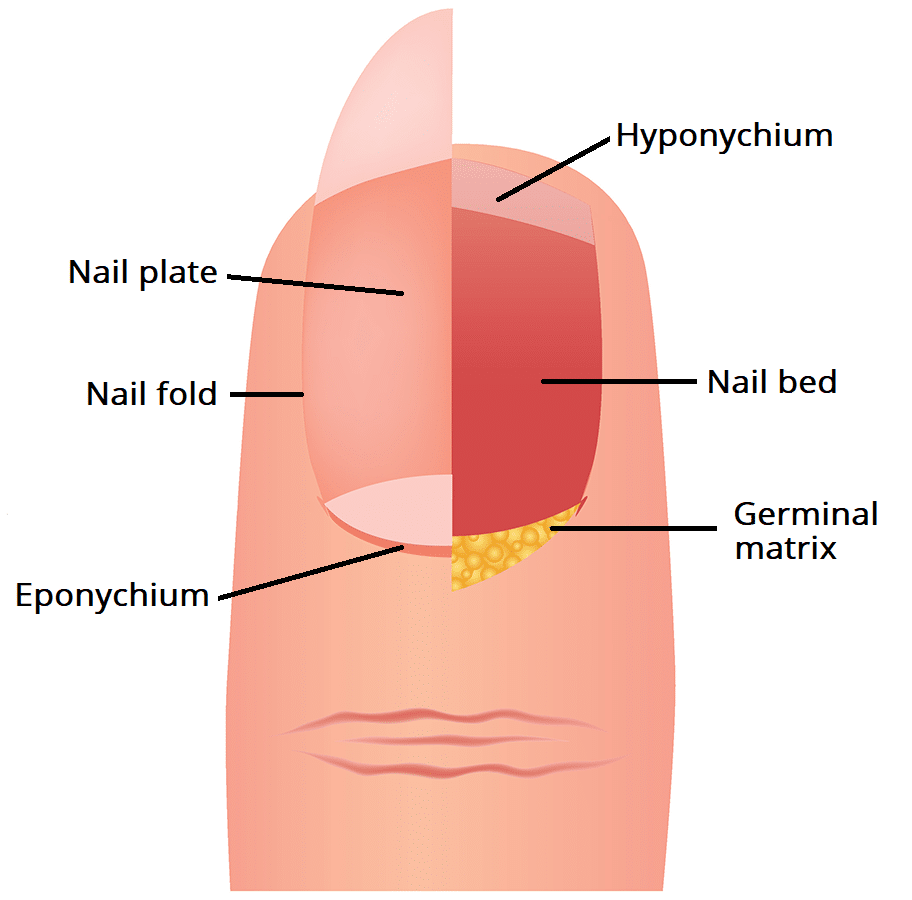
Nails are hard plates made of a protein
called keratin located at the tips of the fingers and toes.
 |
| Image from TeachMeAnatomy |
- Protect the ends of the fingers and toes from
injury.
- Make it easier to pick up small
objects, scratch, and grip things.
- The nail bed underneath
is rich in blood vessels and can show signs of health problems when color
changes.
Nails are
hard covers at the tips of your fingers and toes that protect them and help you
grab things.
Protection
from UV rays and germs
 |
| Image from New Atlas |
The skin protects
your body in several ways:
- Blocking UV rays - melanin in the epidermis absorbs some UV radiation so less reaches deeper cells. People with more melanin usually have darker skin and more natural protection, but everyone can be damaged by too much sun.
- Barrier against pathogens - the unbroken epidermis keeps most bacteria and viruses out. Natural oils and slightly acidic sweat on the surface help slow the growth of germs.
- Repairing damage - when the skin is cut, blood clots form, and new cells grow to close the wound, restoring the protective barrier.
The skin acts
like a shield, blocking many sun rays and germs, and can repair itself when it
gets a cut.
Other
important jobs of the skin
- Sensation - nerve endings in the dermis let you feel touch, pressure, pain, and temperature, helping you react to danger (like something hot or sharp).
- Excretion - sweat glands in the skin remove small amounts of water, salts, and wastes, helping the body get rid of extra materials.
- Vitamin D production - when skin is exposed to sunlight, it helps make vitamin D, which is important for healthy bones.
The skin lets you
feel the world, gets rid of a little waste through sweat, and helps your body
make vitamin D.
Integumentary System Quiz: click here
