Science, Technology, and Society LET REVIEWER
General Education
Lesson 19: Homologous &Analogous Structure
The study of body
structures and how they are used helps scientists understand evolution, adaptation,
and how organisms are related. In this lesson you will learn about homologous
structures, analogous structures, and how humans use biotechnology to
modify living things and solve problems.
- We will compare body parts that are similar or different, and then see how people use biotechnology to change or use living things on purpose.
Homologous Structures
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/about-homologous-structures-1224763_sketch_FINAL2-4c326d5ec6a5440d9224580a5bbe36d7.png) |
| Image from ThoughtCo. |
What are homologous organs?
- Same basic bone pattern or layout.
- Often found in species that are evolutionarily
related.
- Show divergent evolution –
one ancestral structure becomes different forms for different uses.
Examples of homologous
structures:
- Human arm –
used for lifting, carrying, and manipulating objects.
- Cat leg –
used for walking and running on four legs.
- Seal flipper –
used for swimming in water.
- Bat wing –
used for flying.
Even though a human
arm, cat leg, seal flipper, and bat wing all
do different jobs, their bone arrangement (humerus, radius,
ulna, wrist, fingers) is very similar.
Homologous
organs have the same basic design on the inside, but are used for
different jobs in different animals.
Analogous Structures
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/about-analogous-structures-1224491_FINAL-e698155dffc74b0490741d0458585d9f.png) |
| Image from ThoughtCo. |
What are analogous organs?
- Same function,
different design.
- Often found in species that are not
closely related.
- Show convergent evolution –
different ancestors evolve similar solutions to the same problem.
Example of analogous
structures:
- Butterfly’s wings –
made of thin membranes stretched over veins; attached to the exoskeleton;
no bones.
- Bat’s wings –
made of skin stretched between long finger bones; attached to a vertebrate
skeleton.
Both butterfly
wings and bat wings are used for flying,
but their structure and origin are very
different.
Analogous
organs look and work the same on the outside (same job), but are built
differently on the inside and come from different ancestors.
 |
| (Click to Unblur) |
- Homologous - same design, different
use.
- Analogous - same use, different
design.
Why These Structures Matter in Biology
- They help scientists reconstruct
evolutionary history.
- Homologous structures suggest
that organisms share a common ancestor.
- Analogous structures show
how environmental pressures can shape different species
in similar ways.
- Both concepts support the idea
of adaptation and natural selection.
By
comparing body parts, scientists can tell who is “related” and who only looks
similar because they live in similar environments.
Introduction to
Biotechnology
What is biotechnology?
- Uses cells, enzymes, DNA,
and whole organisms.
- Found in medicine, agriculture, food
production, and environmental cleanup.
Biotechnology is
when humans use or change living things on purpose to do useful things.
Genetic Engineering and
GMOs
| Image from MIT |
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering is
a type of biotechnology where scientists change an organism’s DNA directly.
- Specific genes can be cut out, copied,
or inserted.
- This can give the organism a new
trait, such as disease resistance or the ability to make a useful
protein.
GMO / Transgenic organism
- A GMO (genetically modified
organism) or transgenic organism has had
its genes altered or had new genes added by
humans.
- The new gene might come from a different
species.
Examples you might hear
about (in general):
- Crops engineered to resist insects or
herbicides.
- Bacteria engineered to produce human
insulin for diabetes treatment.
In genetic
engineering, scientists edit an organism’s DNA, and the result is a GMO that
has traits it did not have before.
Bioremediation
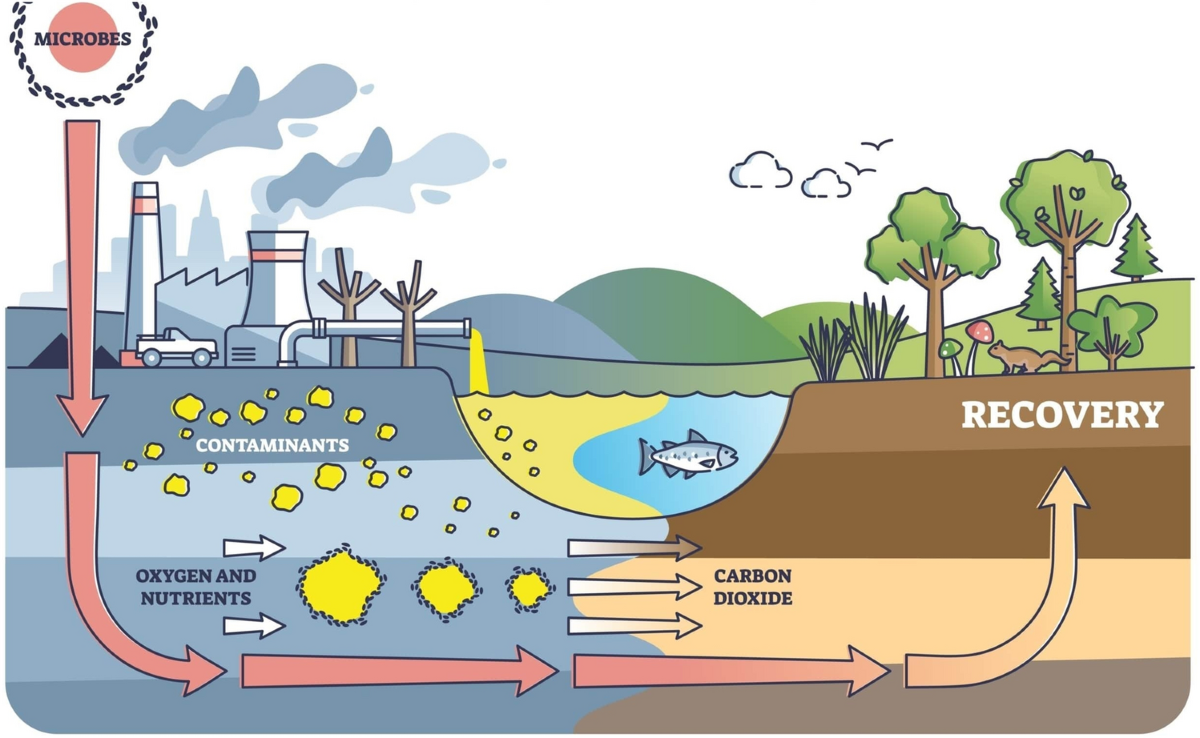 |
| Image from Springer Link |
What is bioremediation?
- Often uses bacteria, fungi,
or plants.
- These organisms use the pollutant as
a food source or change it into something less
harmful.
Example: Oil-eating
bacteria
- Oil-eating bacteria are
used in cleaning up oil spills.
- These bacteria can break down oil
molecules into simpler substances that are less dangerous.
- They help restore oceans and
coastlines after accidents.
Bioremediation uses
living things, like oil-eating bacteria, to clean up messes in the
environment.
Homologous and Analogous Structure Quiz: click here

