Science, Technology, and Society LET REVIEWER
General Education
Lesson 22: Objects in the Universe
Space Rocks, Comets, and Stars
 |
Image from Science Notes
|
1. Asteroids, Meteoroids, Meteors, and Meteorites
In our solar system there are many small rocky objects besides the planets. The largest of these small bodies are called asteroids. They are chunks of rock (and sometimes metal) that orbit the Sun, mostly in a region between Mars and Jupiter called the asteroid belt. Smaller pieces that break off from asteroids (or sometimes comets) are called meteoroids. When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere and burns because of friction with the air, we see a bright streak of light in the sky called a meteor, often nicknamed a “shooting star.” If a meteoroid is large and strong enough that a piece survives its fall and lands on the ground, that leftover piece is called a meteorite.
- Asteroid – rocky object orbiting the Sun, usually in the asteroid belt.
- Meteoroid – small debris chipped off from an asteroid (remember: “roid” = from asteroid).
- Meteor – the bright streak seen when a meteoroid enters the atmosphere and burns.
- Meteorite – the part that hits the land and is found on Earth (“‑ite” like a rock or mineral).
Think of one space rock going through stages: in space it’s a meteoroid, as it burns in the sky it’s a meteor, and if a piece reaches the ground it’s a meteorite.
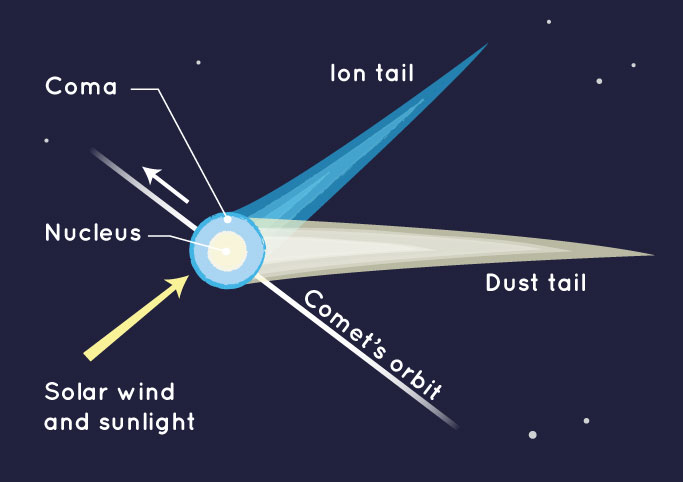 |
Image from Nasa Space
|
2. Comets: “Long‑Haired”
Besides rocky asteroids, there are also icy objects called comets. The word “comet” comes from a term that means “long‑haired”, because early observers thought the glowing tail looked like long hair flowing behind the object. A comet is a small body made of rock, iron, ice, methane, ammonia, and carbon dioxide that orbits the Sun. Far from the Sun, a comet is mostly a dirty ball of ice and dust. When it moves close to the Sun, the heat makes its ices turn into gas, and this gas, along with dust, streams away and forms a bright tail. The important thing to remember is that the tail of a comet always points away from the Sun, because it is pushed by sunlight and the solar wind, not dragged behind like smoke from a moving train.
Near the center of a comet is its solid core. This solid part is called the nucleus, and the cloud of gas and dust that surrounds it when it is warmed by the Sun is called the coma. Together the nucleus and coma make the bright “head” of the comet. Some comets return on regular schedules; a famous one is Halley’s comet, which appears in our sky about every 76 years.
- Comet – icy body of rock, iron, ice, methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide that orbits the Sun.
- Name means “long‑haired” because of its tail.
- Tail points away from the Sun, no matter which way the comet is moving.
- Solid nucleus surrounded by a glowing cloud called the coma.
- Halley’s comet returns roughly every 76 years.
A comet is like a dirty snowball in space. When it gets near the Sun, it heats up and grows a glowing tail that always points away from the Sun.
| Image from Silicon Republic |
3. Stars: Giant Balls of Gas
A star is a huge ball of hot gas, mainly hydrogen and helium, held together by its own gravity. Deep inside the star, the pressure and temperature are so high that hydrogen atoms are forced to join together in a process called nuclear fusion, which releases a tremendous amount of energy. This energy escapes as light and heat, which is why stars shine. Our Sun is an example of a star, but stars come in many different sizes and colors.
The color of a star tells us something about its temperature. The hottest stars look blue, while the coolest stars look red. Stars that are in between can look white, yellow, or orange. So even though we might think of red as a “hot” color in everyday life, in stars it actually means the star is cooler than a blue one.
- Star – a huge ball of hydrogen and helium that produces energy by nuclear fusion.
- Blue stars are the hottest; red stars are the coolest.
- The Sun is a medium‑sized star compared with others.
A star is a massive, glowing ball of gas. Blue stars are hotter, red stars are cooler.
 |
| Image from Constellations Guide |
4. Constellations
When we look at the night sky, it is natural to connect stars into shapes. A constellation is a group of stars forming a recognizable pattern in the sky. Ancient people gave these patterns names based on animals, people, and objects they thought they looked like, and these names are still used today. The stars in a constellation usually are not close to each other in space; they only appear grouped together from our viewpoint on Earth.
Examples of constellations include Ursa Minor (the Little Bear) and Orion, which looks a bit like a hunter with a belt of three bright stars in a row. Within Ursa Minor is an important star called Polaris, also known as the North Star or Northern Star. Polaris is special because it lies almost directly above Earth’s North Pole, so it appears nearly fixed in the sky while other stars seem to turn around it. For centuries, sailors and travelers in the Northern Hemisphere have used Polaris to find the direction north.
- Constellation – group of stars forming a recognizable pattern.
- Examples: Ursa Minor, Orion, and many others.
- Polaris (Northern Star) is in Ursa Minor and points approximately to north.
A constellation is like a “picture” made of stars. Polaris in Ursa Minor helps us know which way is north.
 |
| Image from BBC Sky |
5. Stars: Nearest, Brightest, and Largest
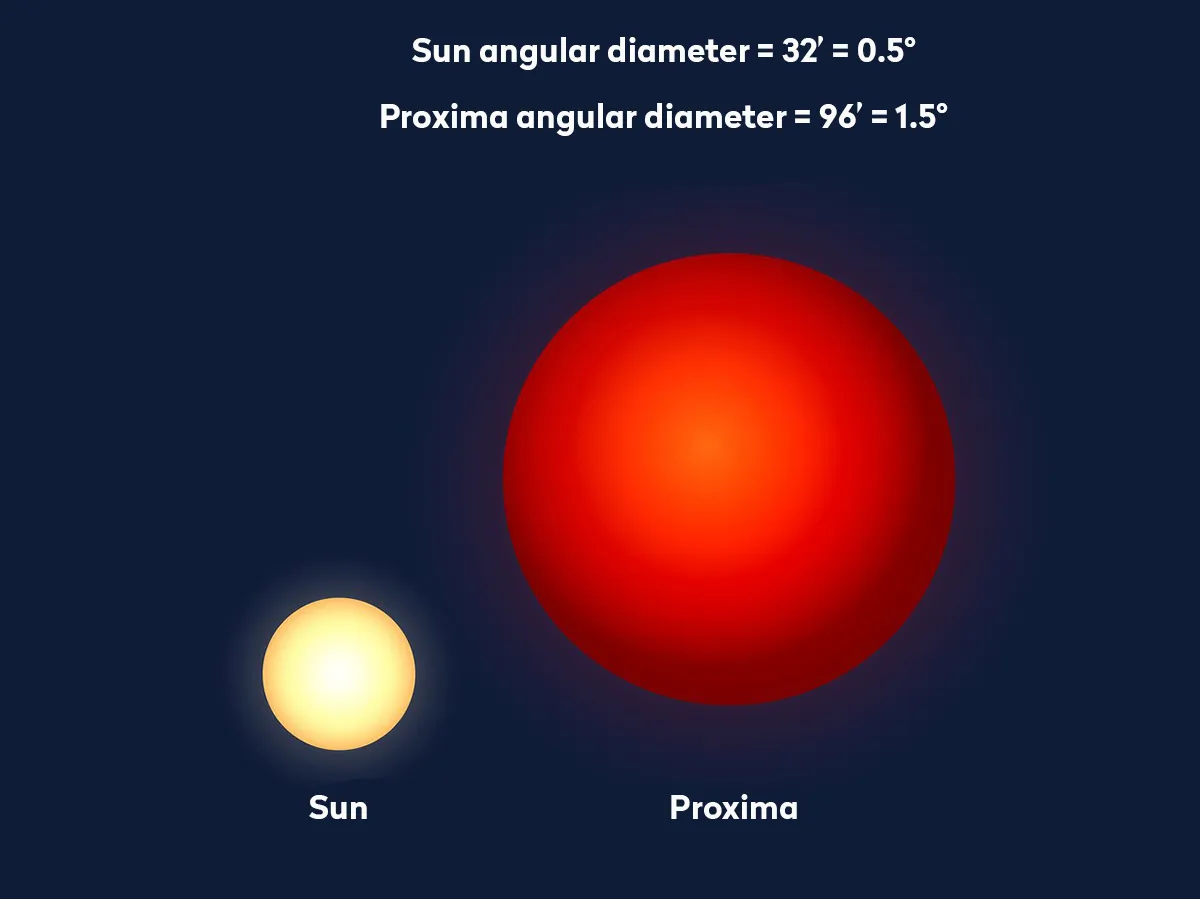
Besides our Sun, other stars have special records in the sky. The nearest star to Earth (other than the Sun) is Proxima Centauri. It is part of a small group of stars called Alpha Centauri and is still so far away that its light takes about four years to reach us. Even though it is our closest stellar neighbor, Proxima Centauri is faint and can’t be seen without a telescope.
The brightest star in our night sky (as seen from Earth) is Sirius. Sirius is found in the constellation Canis Major (the Big Dog), which is why it is sometimes called the “Dog Star.” Sirius looks very bright not because it is the largest star, but because it is fairly close to us and shines strongly.
Astronomers have also discovered stars that are extremely large compared to our Sun. One of the biggest known is Stephenson 2‑18, which is classified as a red supergiant. If Stephenson 2‑18 were placed where our Sun is, it would extend far beyond the orbit of Earth and many of the other inner planets. Stars like this show the huge range of sizes that stars can have.
- Proxima Centauri – nearest star to Earth after the Sun.
- Sirius – brightest star in our night sky.
- Polaris – Northern Star, used for navigation, part of Ursa Minor.
- Stephenson 2‑18 – one of the largest known stars.
Proxima Centauri is our closest stellar neighbor, Sirius looks the brightest in our sky, Polaris points north, and Stephenson 2‑18 is an enormous star that makes our Sun look small.
RECAP:
- Space rocks: Asteroid → Meteoroid → Meteor → Meteorite (life cycle from belt to ground).
- Comets with comas and tails pointing away from the Sun.
- Stars made of hydrogen and helium, with colors showing temperature.
- Star patterns: Constellations and special stars used for navigation and study of the universe.
Object in the Universe Quiz
