Science, Technology, and Society LET REVIEWER
General Education
Lesson 18: Genetics
What is Genetics?
Genetics is the study of genes and heredity,
which means how traits are passed from parents to offspring.
Traits include things like eye color, height, hair
texture, and even some diseases.
Genetics explains
why you look a bit like your mother, your father, or other relatives.
The Father of Genetics
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian
monk who experimented with pea plants in the 1800s. By
carefully crossing plants with different traits (like tall vs. short), he
discovered the basic rules of inheritance, so he is called
the Father of genetics.
Gregor
Mendel was the scientist who first figured out how traits are passed
from parents to children.
Trait, Gene, Allele, and Character
 |
| Image from Adobe Stock |
Before we use the new words, it helps to connect them:
- A character is
a feature, like height or seed shape.
- A trait is
a specific form of that character, like tall or short.
- A gene is
a segment of DNA that controls a character.
- An allele is
a different version of a gene (for example, one allele
for straight hair and one for kinky hair).
A gene is
like a “recipe” for a trait, and alleles are different
versions of that recipe.
Phenotype and Genotype
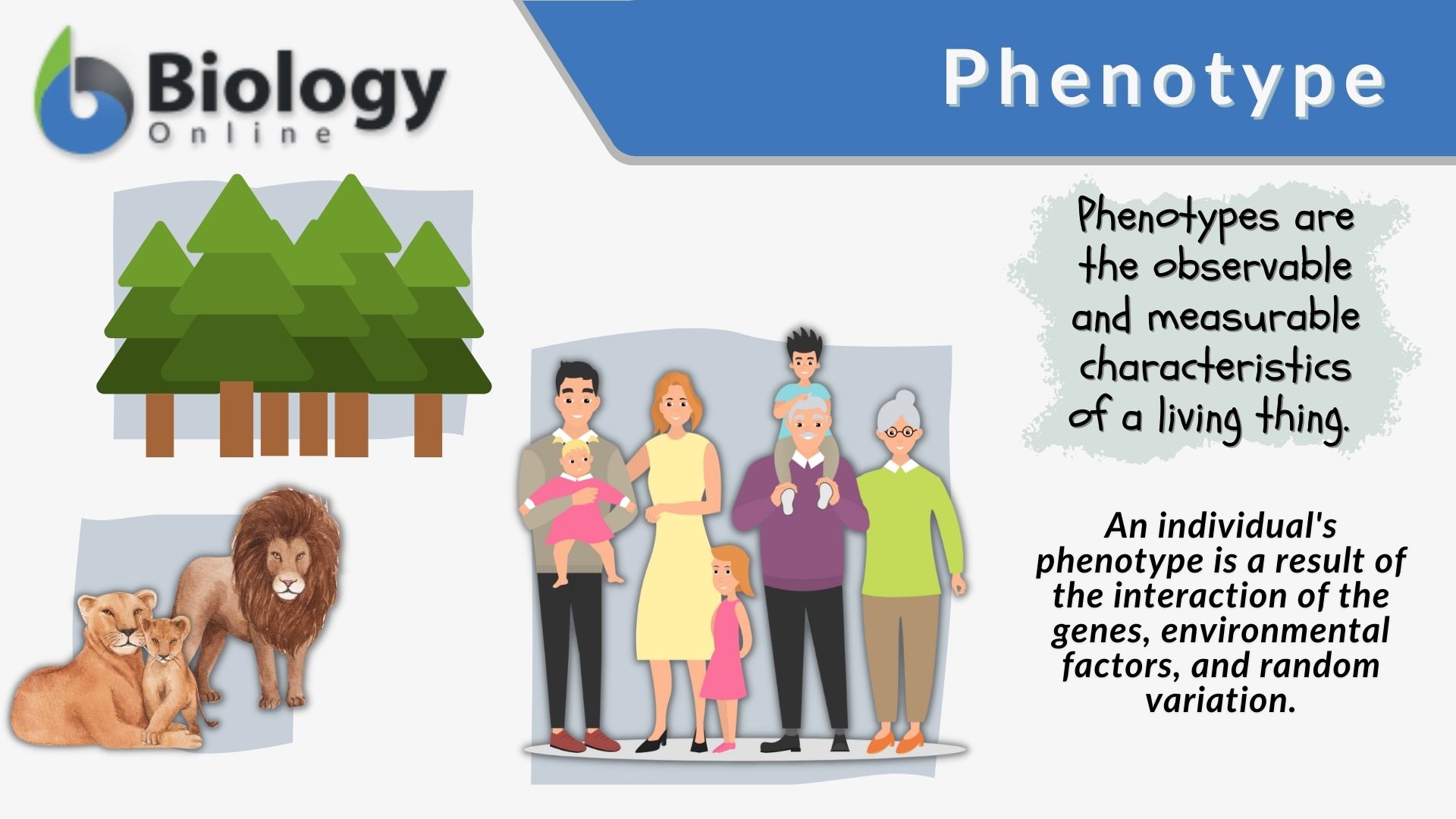
Phenotype
 |
| Image from Biology Online |
- Examples
of phenotype: green, tall, short, straight
hair, kinky hair.
Phenotype is
what a trait looks like on the outside.
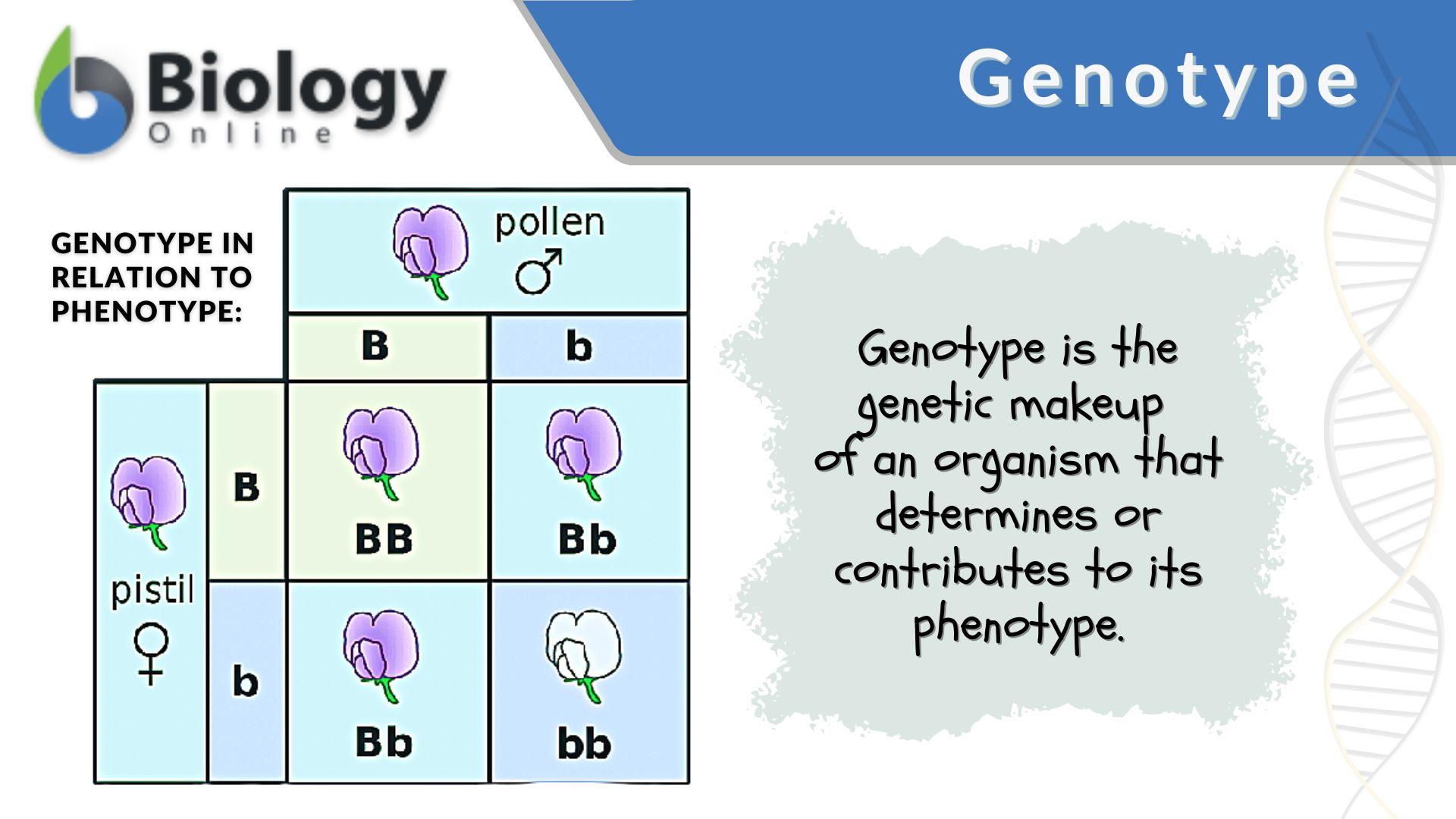
Genotype
 |
| Image from Biology Online |
- Examples
of genotype: Gg, gg, HH, hh.
- Capital
letter = usually the dominant allele.
- Small
letter = usually the recessive allele.
Genotype is
the hidden gene code that you cannot see directly, but it controls the
phenotype.
Homozygous and Heterozygous
An organism has two alleles for each gene
(one from each parent).
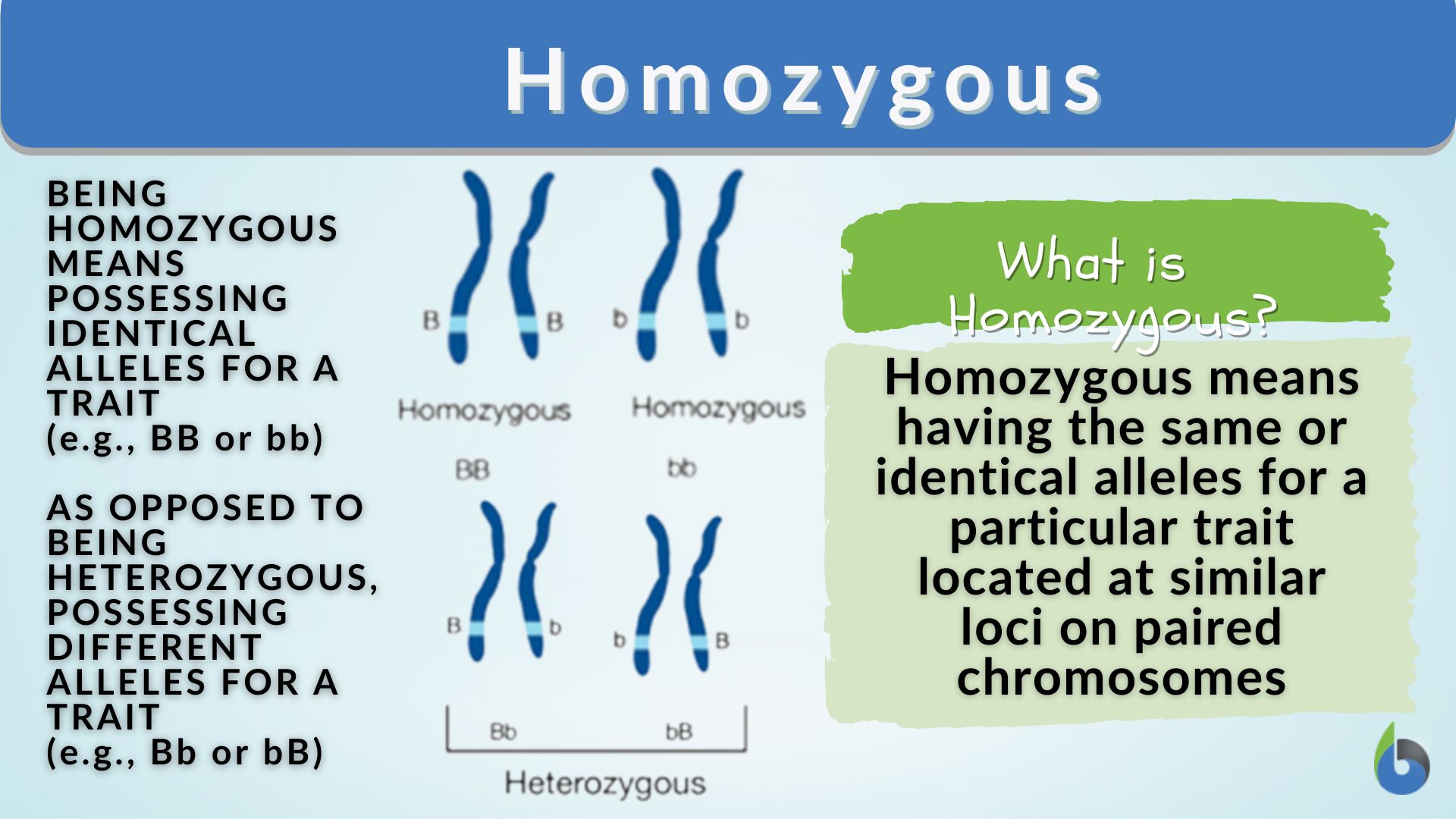
Homozygous
 |
| Image from Biology Online |
Homozygous means the two
alleles are the same.
- Examples
of homozygous genotypes: HH, TT, tt.
- Can
be homozygous dominant (HH, TT) or homozygous
recessive (tt, hh).
Homozygous means
“same-same” letters for a gene.
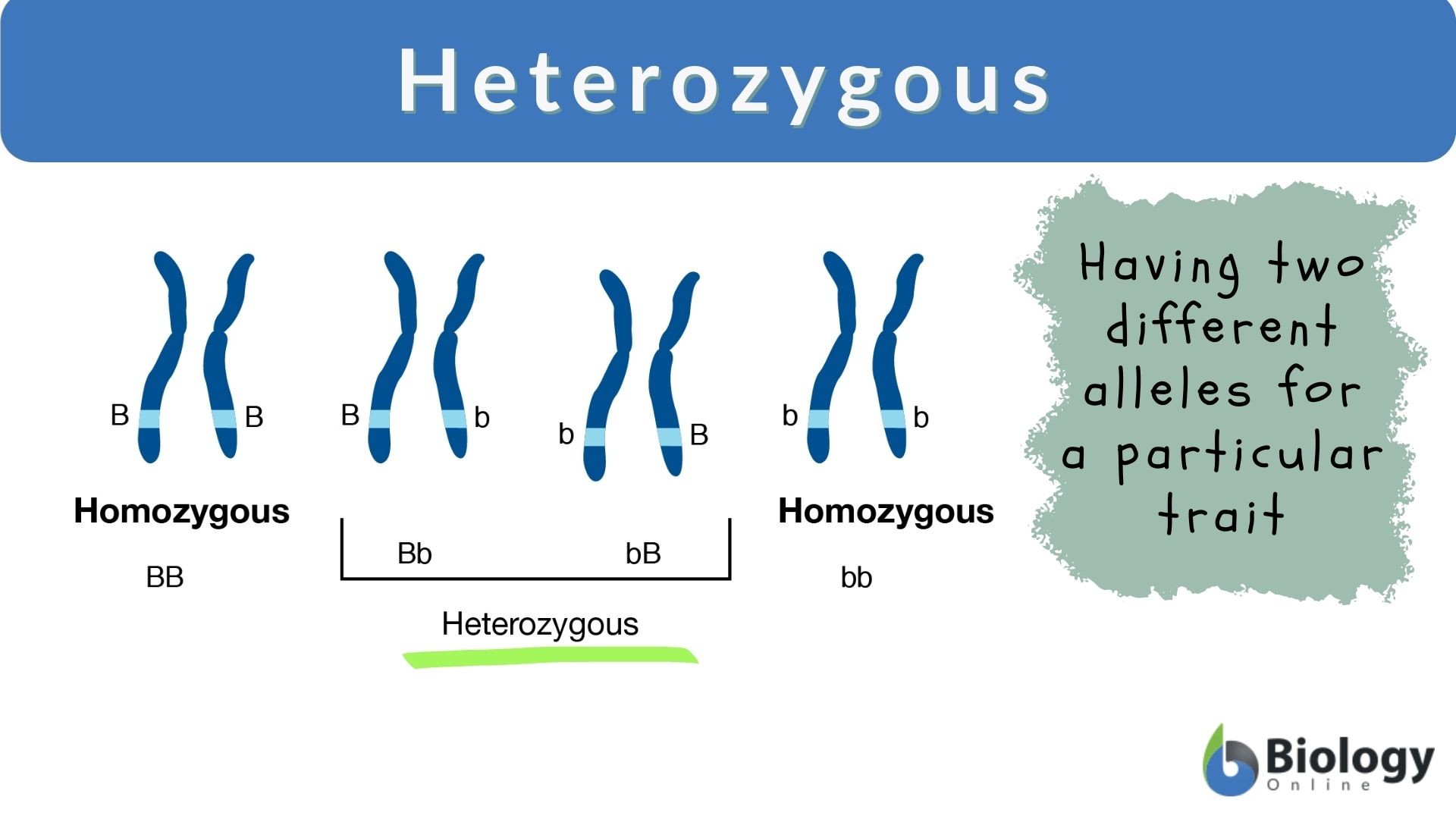
Heterozygous
 |
| Image from Biology Online |
Heterozygous means the two
alleles are different.
- Examples
of heterozygous genotypes: Hh, Tt.
- One
allele is dominant, and the other is recessive.
Heterozygous means
“different” letters for a gene, like one capital and one small letter.
Mendel’s Law of Dominance
Mendel’s Law of Dominance explains
how dominant and recessive genes work
together.
 |
| Image from Expii |
Dominant Gene
- A dominant
gene is like a working gene that prevents
the expression of the other gene (the recessive gene).
- It
is written with a capital letter (for example, S).
- If
a dominant gene is present, its trait shows in the
phenotype.
A dominant
gene is strong and “shows up” whenever it is present.
Recessive Gene
- A recessive
gene is like a non-working gene that is masked when
a dominant gene is present.
- It
is written with a lowercase letter (for example, s).
- It
will only have phenotypic expression (be seen) if there
are two recessive alleles – a homozygous
recessive genotype (like ss).
A recessive
gene is shy and only shows when it is paired with another recessive
gene.
Example Trait: Straight vs. Kinky Hair
 |
| Image from iStock |
- S – Straight hair
(Dominant)
- s – Kinky hair
(Recessive)
Possible Genotypes and Phenotypes
- SS –
both alleles are dominant
- Genotype: homozygous
dominant
- Phenotype: Straight hair
- Ss –
one dominant and one recessive allele
- Genotype: heterozygous
- Phenotype: Straight hair
(dominant covers recessive)
- ss –
both alleles are recessive
- Genotype: homozygous
recessive
- Phenotype: Kinky hair
Summary for this example:
- SS
→ Straight
- Ss
→ Straight
- ss
→ Kinky
If
at least one S is present (SS or Ss), the hair is straight.
You only see kinky hair when both letters are s (ss).
Punnett Square (Optional Visual Practice)
You can use a Punnett square to predict
offspring genotypes when two parents have children.
Example: Parent Genotypes
- Parent
1: Ss (Straight hair)
- Parent
2: Ss (Straight hair)
Punnett square (each box is a possible child):
|
|
S |
s |
|
S |
SS |
Ss |
|
s |
Ss |
ss |
- 1
SS – Straight (homozygous dominant)
- 2
Ss – Straight (heterozygous)
- 1
ss – Kinky (homozygous recessive)
So, in theory, their children have:
- 3
out of 4 chance of Straight hair (SS or Ss)
- 1
out of 4 chance of Kinky hair (ss)
A Punnett
square is a simple table that helps predict what genotypes and
phenotypes the children might have.
Genetics Quiz: click here

